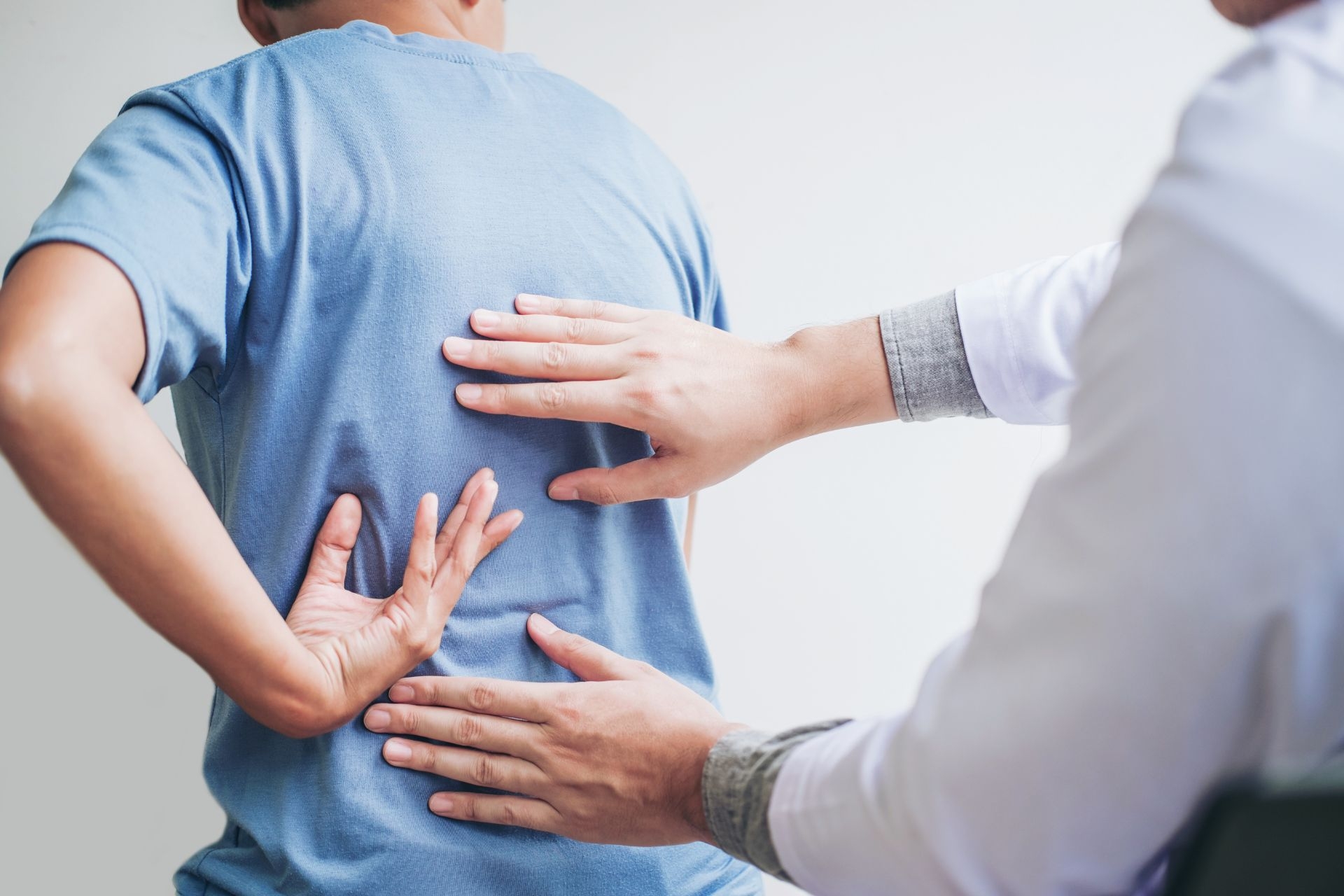

Myofascial release is a therapeutic technique that focuses on releasing tension and restrictions in the fascia, a connective tissue that surrounds and supports muscles, bones, and organs in the body. It involves applying gentle pressure and stretching to the affected areas to help release tightness and improve mobility. Myofascial release works by targeting the fascia, which can become tight and restricted due to factors such as injury, trauma, or repetitive movements. By releasing these restrictions, myofascial release can help improve blood flow, reduce pain, and restore proper function to the affected area.
The benefits of myofascial release therapy are numerous. Firstly, it can help alleviate pain and discomfort caused by tight or restricted fascia. By releasing tension in the fascia, myofascial release can help reduce muscle soreness, improve flexibility, and enhance overall movement. Additionally, myofascial release can improve circulation and lymphatic drainage, which can aid in the removal of toxins and waste products from the body. Pain Neuroscience Education This therapy can also help improve posture and alignment, as well as enhance athletic performance. Overall, myofascial release therapy offers a holistic approach to addressing musculoskeletal issues and promoting overall well-being.
Yes, myofascial release can be beneficial for individuals with chronic pain conditions. Vestibular Testing Chronic pain often stems from tightness and restrictions in the fascia, which can lead to muscle imbalances and dysfunction. Myofascial release therapy can help release these restrictions, reduce pain, and improve mobility. It can also help address underlying issues that contribute to chronic pain, such as poor posture or repetitive movements. However, it is important to note that individual results may vary, and it is recommended to consult with a healthcare professional to determine if myofascial release is appropriate for your specific condition.
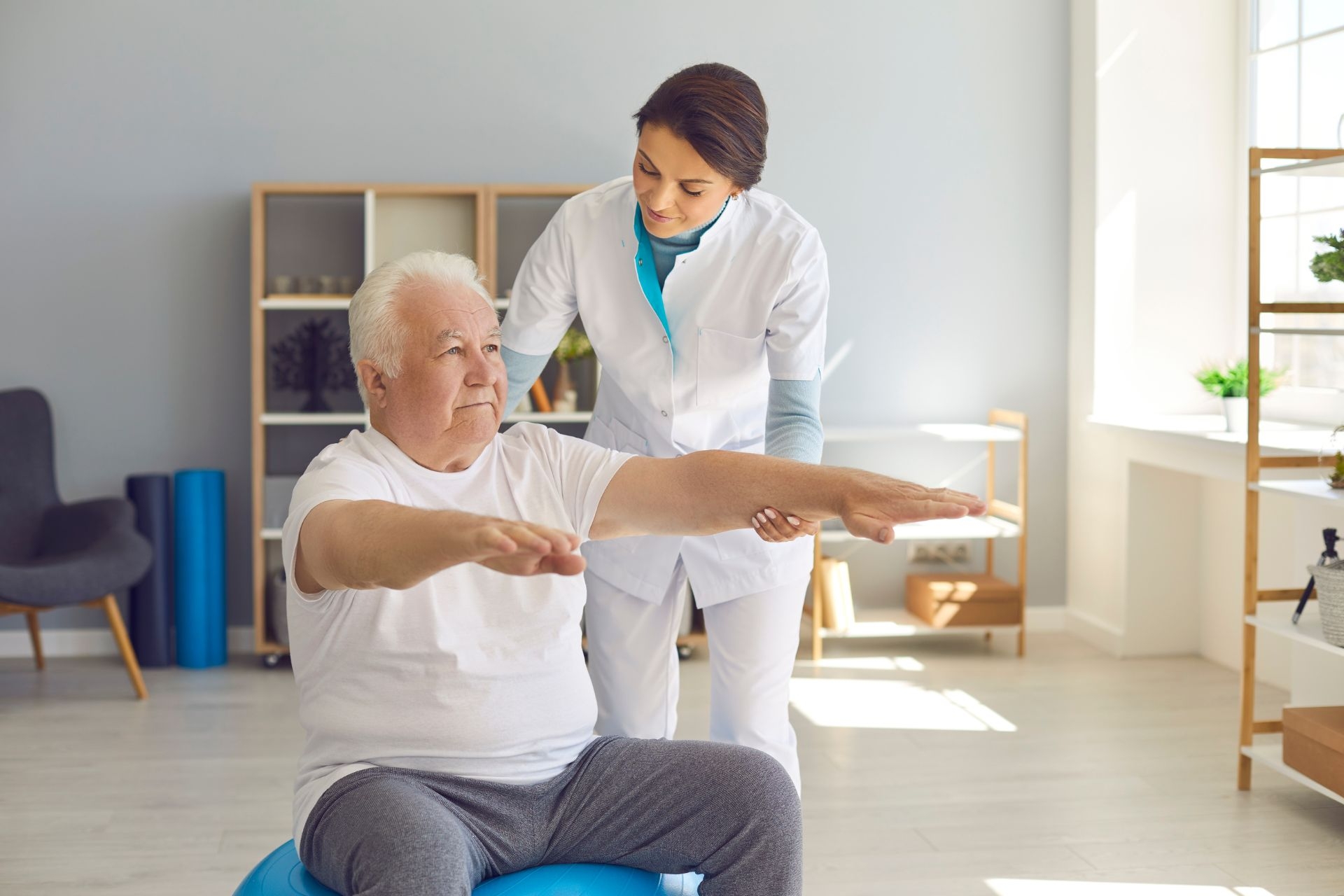

When performed by a trained professional, myofascial release is generally considered safe and low risk. However, there are some potential risks and side effects to be aware of. In rare cases, individuals may experience temporary soreness, bruising, or swelling after a myofascial release session. It is also possible to experience a temporary increase in pain or discomfort during the treatment as the fascia is being released. Post-Concussion Therapy It is important to communicate any concerns or discomfort with your therapist during the session to ensure a safe and effective treatment.
The duration of a typical myofascial release session can vary depending on the individual and the specific needs of the treatment. Sessions can range from 30 minutes to an hour or longer. During the session, the therapist will assess the areas of tension and apply gentle pressure and stretching techniques to release the fascia. Running Analysis The therapist may also provide guidance on self-care techniques and exercises to continue the benefits of the treatment at home. It is recommended to discuss the duration of the session with your therapist to ensure adequate time for your specific needs.
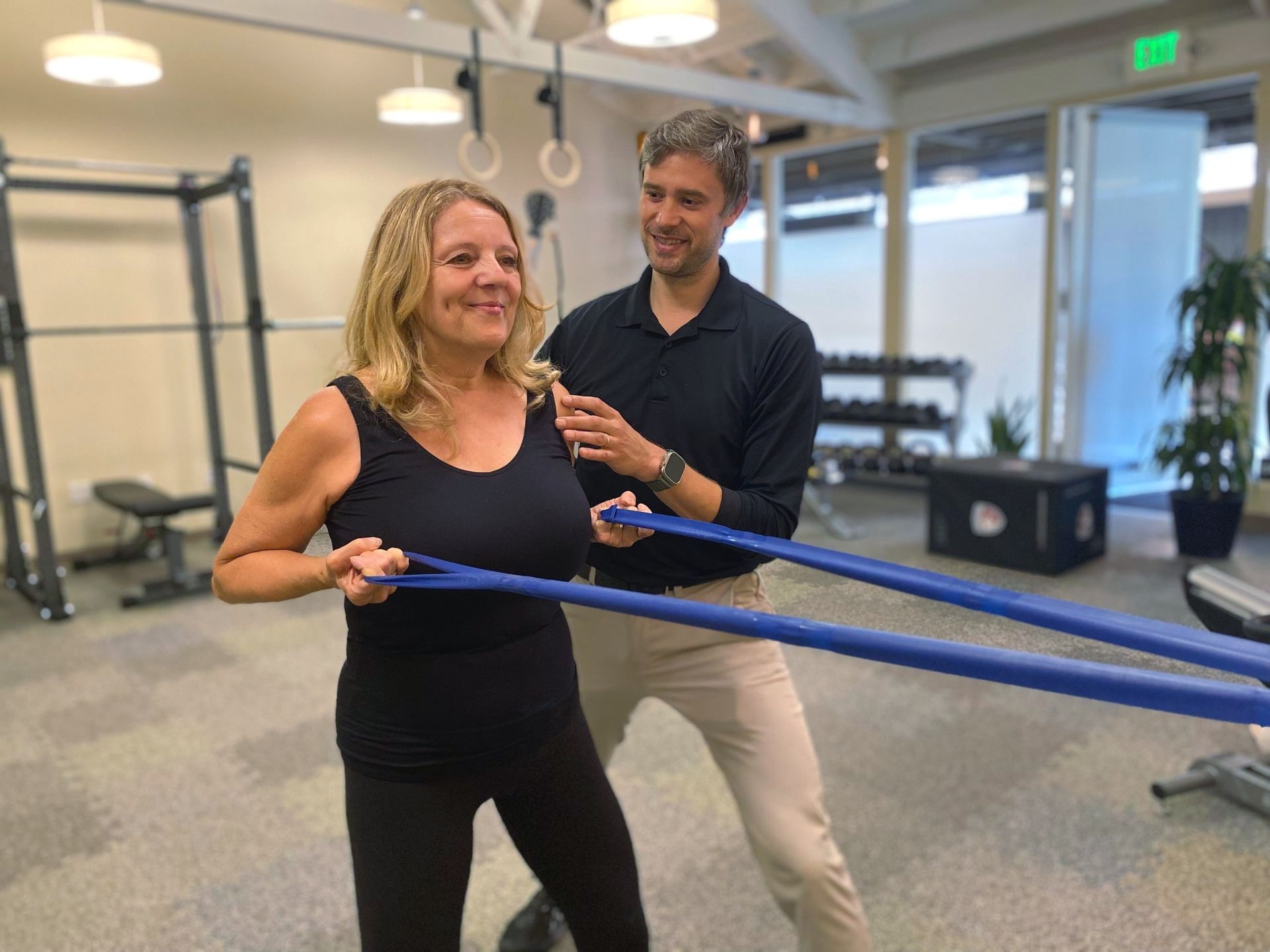

While myofascial release is generally safe and beneficial for most individuals, there are some contraindications to consider. Electrical Stimulation Individuals with certain medical conditions, such as blood clotting disorders or active infections, may need to avoid myofascial release or seek clearance from their healthcare provider. Additionally, individuals with certain types of cancer or recent surgeries may need to avoid or modify the treatment. It is important to disclose any relevant medical history or conditions to your therapist before starting myofascial release therapy to ensure a safe and effective treatment.
Yes, myofascial release can be used in conjunction with other therapies or treatments. It is often integrated into a comprehensive treatment plan that may include other modalities such as physical therapy, chiropractic care, or massage therapy. Myofascial release can complement these treatments by addressing the fascial restrictions and promoting overall healing and recovery. It is important to communicate with your healthcare providers to ensure coordination of care and to determine the most appropriate combination of therapies for your specific needs.

Physical therapy plays a crucial role in the management of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) by addressing the various physical impairments and functional limitations associated with the disease. Through a comprehensive evaluation, physical therapists develop individualized treatment plans that focus on maintaining and improving mobility, strength, and overall physical function. They may employ a range of techniques, including therapeutic exercises, stretching, range of motion exercises, and balance training, to help manage muscle weakness, spasticity, and loss of coordination. Additionally, physical therapists may utilize assistive devices and adaptive equipment to enhance independence and optimize daily activities. By working closely with patients, physical therapists aim to maximize their quality of life and promote overall well-being.
Physical therapy plays a crucial role in managing post-polio syndrome by addressing the specific needs and challenges faced by individuals with this condition. Through a comprehensive evaluation, physical therapists can assess the patient's functional abilities, muscle strength, range of motion, and balance. Based on the assessment findings, they develop personalized treatment plans that may include exercises to improve muscle strength and endurance, stretching to maintain or improve flexibility, and balance training to reduce the risk of falls. Additionally, physical therapists may use modalities such as heat or cold therapy, electrical stimulation, or ultrasound to alleviate pain and promote tissue healing. They also educate patients on energy conservation techniques and assistive devices to optimize their daily activities and minimize fatigue. By providing targeted interventions, physical therapy helps individuals with post-polio syndrome enhance their overall quality of life and maintain their independence.
Physical therapists take a comprehensive and individualized approach to rehabilitation following hip arthroscopy. They begin by assessing the patient's specific condition, including the extent of the hip joint damage, any associated muscle imbalances, and the patient's overall functional goals. Based on this assessment, the physical therapist develops a tailored treatment plan that may include a combination of manual therapy techniques, therapeutic exercises, and modalities such as heat or ice therapy. The therapist focuses on improving range of motion, strength, and stability of the hip joint, while also addressing any compensatory movement patterns or muscle imbalances that may have developed. They may also incorporate functional training exercises to help the patient regain their ability to perform daily activities and return to their desired level of physical activity. Throughout the rehabilitation process, the physical therapist closely monitors the patient's progress and adjusts the treatment plan as needed to ensure optimal outcomes.
Physical therapists play a crucial role in helping individuals with tibial stress fractures recover and regain their mobility. They employ a variety of techniques and interventions to address the specific needs of each patient. Initially, physical therapists may use modalities such as ice or heat therapy to reduce pain and inflammation in the affected area. They may also utilize manual therapy techniques, such as soft tissue mobilization or joint mobilization, to improve tissue healing and restore normal joint mechanics. Additionally, physical therapists design individualized exercise programs that focus on strengthening the muscles surrounding the tibia, improving flexibility, and gradually increasing weight-bearing activities. These exercises may include low-impact activities like swimming or cycling, as well as weight-bearing exercises like walking or jogging. By closely monitoring the patient's progress and adjusting the treatment plan as needed, physical therapists help individuals with tibial stress fractures recover safely and efficiently.
Physical therapy can be an effective treatment option for individuals experiencing patellar dislocation and instability. Through a comprehensive rehabilitation program, physical therapists can address the underlying causes of the condition and help improve patellar tracking and stability. This may involve a combination of exercises to strengthen the muscles around the knee, such as the quadriceps and hamstrings, as well as stretching and flexibility exercises to improve joint mobility. Additionally, physical therapists may utilize modalities such as ice, heat, or electrical stimulation to reduce pain and inflammation. By working closely with a physical therapist, individuals with patellar dislocation and instability can benefit from a personalized treatment plan that aims to restore function and prevent future episodes of dislocation.
Physical therapy can be beneficial in the management of Guillain-Barré syndrome. This neurological disorder affects the peripheral nervous system and can result in muscle weakness and paralysis. Physical therapy aims to improve mobility, strength, and function through various interventions such as exercises, stretching, and manual therapy techniques. It can help individuals with Guillain-Barré syndrome regain muscle strength, improve balance and coordination, and enhance overall physical function. Additionally, physical therapists can provide education on energy conservation techniques and assistive devices to optimize independence and quality of life for individuals with Guillain-Barré syndrome.
Physical therapy can be highly beneficial for individuals with arthrogryposis, a condition characterized by joint contractures and muscle weakness. Through a combination of targeted exercises, stretching, and manual therapy techniques, physical therapists can help improve joint mobility, increase muscle strength, and enhance overall functional abilities. Additionally, physical therapy can assist in managing pain, improving posture and balance, and promoting independence in daily activities. By tailoring treatment plans to address the specific needs and limitations of each individual, physical therapy can play a crucial role in optimizing the quality of life for those with arthrogryposis.
Physical therapy plays a crucial role in assisting individuals with hip osteoarthritis by providing targeted interventions to alleviate pain, improve mobility, and enhance overall function. Through a combination of manual therapy techniques, therapeutic exercises, and modalities such as heat or cold therapy, physical therapists aim to reduce joint inflammation, increase joint range of motion, and strengthen the surrounding muscles. They may also incorporate gait training and balance exercises to improve stability and reduce the risk of falls. Additionally, physical therapists educate patients on proper body mechanics and joint protection strategies to minimize further damage and optimize long-term joint health. By tailoring treatment plans to the specific needs of each individual, physical therapy empowers patients to actively manage their condition and improve their quality of life.